
Bridging the Gap Between Supply and Demand
Millets, often referred to as ‘nutri-cereals,’ have long been a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture and nutrition in adverse climatic regions. However, despite their potential to combat food insecurity and enhance farmer incomes, challenges surrounding Millets Germplasm Supply Demand persist. The crux of the issue lies in insufficient collection and evaluation of germplasm, limited breeding programs for high-yield and nutrient-rich varieties, and the continued use of low-quality seeds. Farmers often relegate millets to rainfed and marginal lands, further exacerbating the Millets Germplasm Supply Demand challenges. Here’s how we can address this pressing issue with strategies for various stakeholders:
For Farmers
1. Training and Awareness
- Conduct village-level campaigns on the importance of using certified seeds and cultivating high-yield varieties.
- Share success stories of farmers who have benefited from improved millet cultivation practices.
2. Access to Quality Inputs
- Develop community seed banks with high-yield and nutrient-rich millet varieties.
- Subsidize quality seeds and fertilizers tailored for millets to encourage adoption.

3. Crop Diversification Programs
- Encourage intercropping millets with other crops to maximize land productivity while conserving resources.
- Provide technical support to farmers on sustainable farming techniques for millets.
For Researchers and Breeders
1. Comprehensive Germplasm Collection and Evaluation
- Initiate multi-location field trials for a broad spectrum of millet germplasm to identify varieties with optimal yield, resilience, and nutritional value.
- Focus on breeding programs that improve traits such as drought tolerance, pest resistance, and enhanced nutritional profiles.
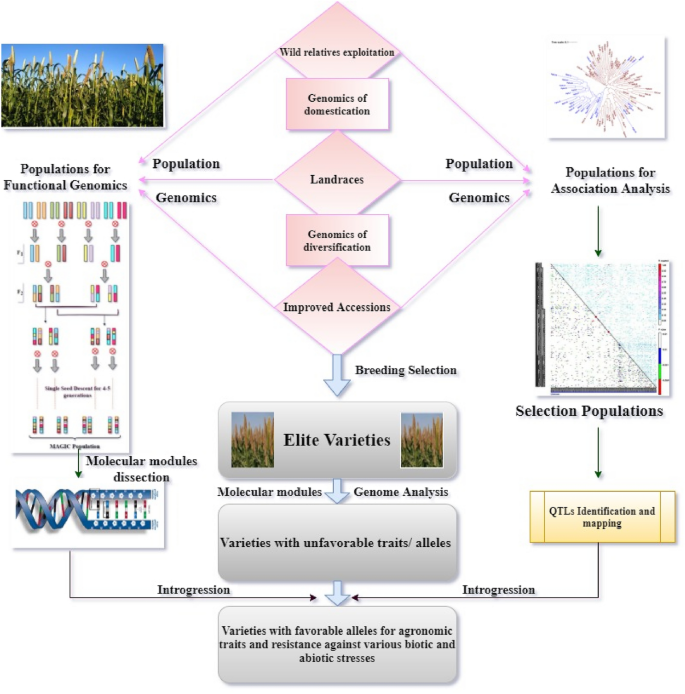
Image Credits: link.springer.com
2. Nutritional Profiling and Biofortification
- Invest in research to develop biofortified millet varieties rich in iron, calcium, and zinc to address malnutrition.
- Promote partnerships between agricultural research institutes and food industries for product development.
3. Data-Driven Innovations
- Create a centralized database of millet germplasm with detailed performance metrics across agro-climatic zones.
- Leverage AI and satellite imagery to optimize millet cultivation practices and predict yield patterns.
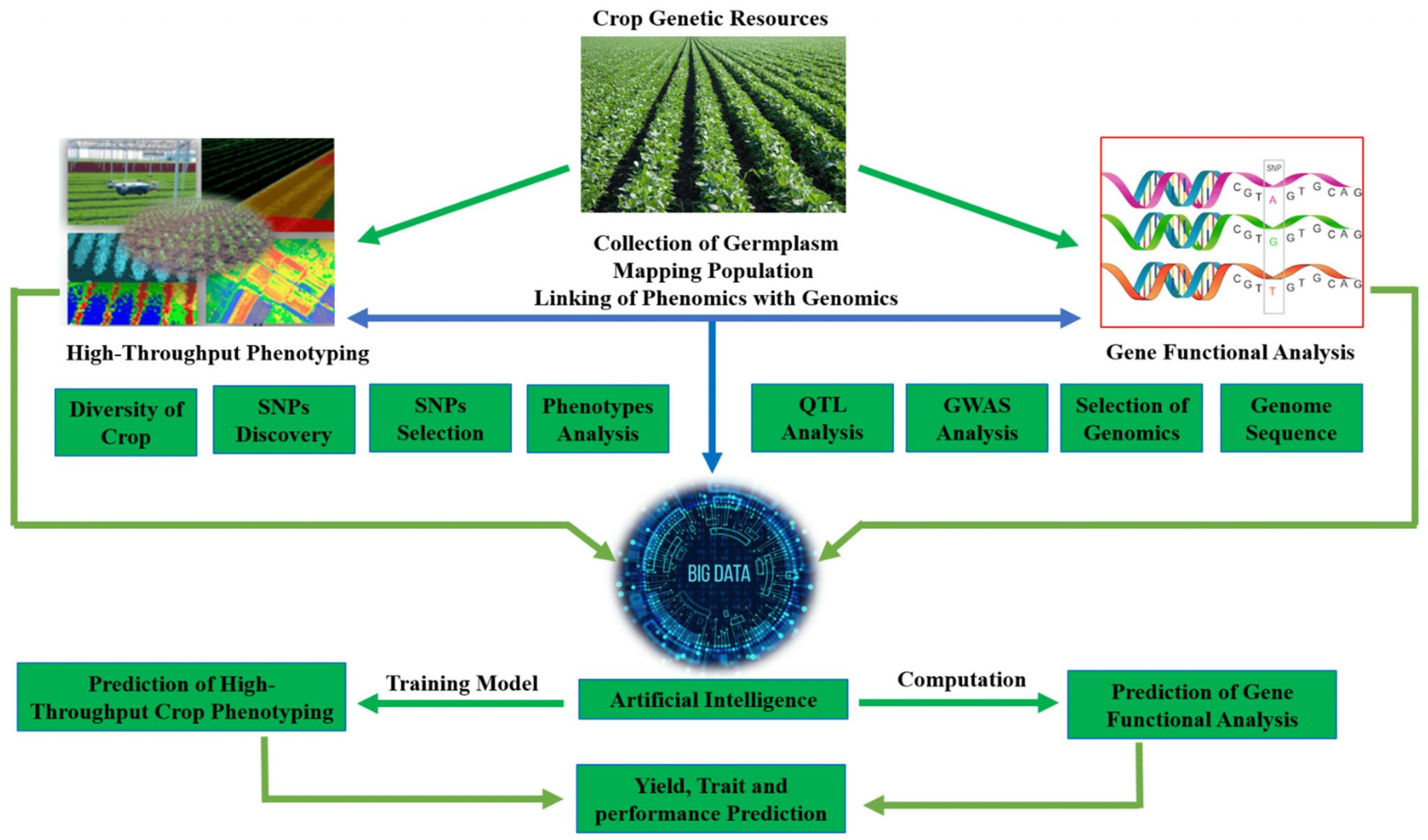
Image Credits: mdpi
For Government and Policy Makers
1. Policy Interventions and Incentives
- IS360 is working on creating virtual forums where small EV companies can
- Introduce minimum support prices (MSPs) for millets to reduce market risks for farmers.
- Provide tax incentives for agritech companies and startups focused on millet innovation.
- Mandate the inclusion of millets in public distribution systems (PDS), mid-day meals, and other welfare programs to create consistent demand.
- exchange insights on industry best practices, innovative technologies, and policy updates.
2. Infrastructure Development
- Establish millet processing units in rural areas to reduce post-harvest losses and enhance value addition.
- Improve rural market linkages through digital platforms to connect farmers directly with consumers.
3. Capacity Building Programs
- Launch farmer field schools and extension services focused on millet cultivation best practices.
- Foster collaborations with international agricultural organizations to adopt global best practices.

For Entrepreneurs and Industry Stakeholders
1. Promoting Value-Added Products
Develop ready-to-eat and ready-to-cook millet products that cater to modern dietary preferences.
Encourage branding and marketing campaigns emphasizing millets as superfoods.

2. Establishing Millet Cooperatives
Create farmer-producer organizations (FPOs) to collectively market millets, negotiate better prices, and access funding.
Facilitate partnerships between cooperatives and food processing companies.
3. Capacity Building Prog3. Investments in AgriTech rams
Support startups using IoT and precision agriculture to optimize millet farming.
Encourage investments in machinery for efficient millet sowing, harvesting, and processing.
For Government and Recommendations to Policy Makers and Government Agencies Policy Makers
1. Launch a National Millet Mission
Similar to the Green Revolution, dedicate funds and resources specifically for millet development, focusing on germplasm conservation and high-yield variety development.
2. Enhance Research and Development
Allocate funds to agricultural universities and ICAR for millet research, particularly in the area of molecular breeding.
3. Promote Millets as a Climate-Resilient Crop
Incorporate millets into climate adaptation plans, emphasizing their ability to thrive in marginal lands.
4. Millets in Urban Diets
Conduct campaigns to make millets mainstream in urban households, emphasizing health benefits and affordability.

5. Strengthen International Collaborations
Partner with global research bodies to share germplasm data and breeding techniques.
By implementing these strategies, millets can transition from being a marginalized crop to a pivotal player in ensuring food security, enhancing rural incomes, and addressing malnutrition.
A concerted effort involving farmers, researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders will be key to unlocking the full potential of nutri-cereals.
IS360 Can be Reached at
Sharing is caring!

