
The Economics of the Millet Ecosystem
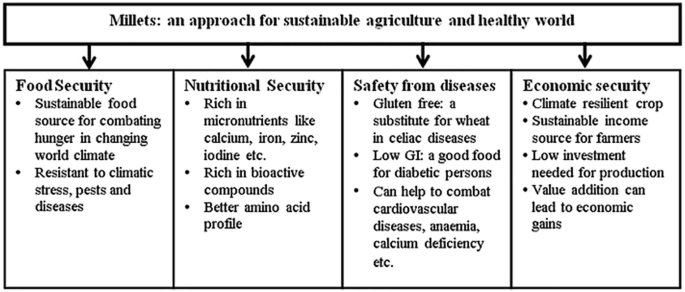
The millet ecosystem, or “Milletnomics,” encompasses the entire value chain of millet production, from cultivation to consumption. Millets, including sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet, and others, are highly resilient, nutritious, and environmentally sustainable grains.
The economic dynamics of millet production involve several key aspects:
1. Cultivation and Production:
- Low Input Costs: Millets require fewer inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides compared to other staple crops like rice and wheat.
Climate Resilience: They thrive in arid and semi-arid regions, making them suitable for regions with unpredictable rainfall.

2. Processing and Value Addition:
- Processing Units: Establishing small-scale processing units can enhance the value of raw millet by transforming it into flour, snacks, ready-to-eat meals, etc.
Innovation in Products: Developing a variety of millet-based products can attract diverse consumer bases, increasing market demand.


3. Market Dynamics:
- Demand and Supply: The demand for millets is driven by their health benefits, while supply is influenced by agricultural practices and climatic conditions.
Price Fluctuations: Prices can be volatile due to seasonal production and varying levels of consumer awareness and acceptance.

4. Government Policies and Support:
- Subsidies and Incentives: Government support in the form of subsidies, minimum support prices (MSP), and incentives for millet cultivation and processing.
Promotional Campaigns: Initiatives to promote millets as part of a healthy diet, particularly during the International Year of Millets.
5. Sustainability:
- Environmental Impact: Millets contribute to sustainable agriculture by improving soil health and reducing dependency on water and chemical inputs.
Socio-economic Impact: They offer livelihood opportunities for small farmers and rural communities, promoting food security and economic stability.


Key Steps for Millet Startups to Sustain in the Ecosystem
1. Cluster-Based Approach:
District-Level Clusters: Form clusters of farmers, processors, and manufacturers within districts to have full control over raw millet prices from the farm level.
Uniform Pricing: Ensure uniform pricing for millet products through coordinated efforts within the cluster, preventing price fluctuations and ensuring fair returns.
2. Identify Niche Markets:
Focus on health-conscious consumers and niche markets such as gluten-free, organic, and vegan food segments.
Leverage the growing trend of functional foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition.
3. Product Innovation:
Develop diverse millet-based products such as ready-to-eat meals, snacks, beverages, and bakery items.
Invest in R&D to improve product quality, taste, and convenience.

4. Build Strong Supply Chains:
Establish reliable procurement networks with farmers to ensure consistent supply and fair prices.
Implement quality control measures to maintain product standards.
Imagecredits:SpringerLink
5. Leverage Technology:
Utilize digital platforms for marketing, sales, and distribution.
Adopt modern agricultural practices and processing technologies to enhance productivity and efficiency.
6. Marketing and Awareness:
Conduct awareness campaigns highlighting the health benefits and sustainability of millets.
Collaborate with nutritionists, chefs, and influencers to promote millet-based products.

7. Government Collaboration:
Engage with government programs and schemes that support millet cultivation and processing.
Apply for grants, subsidies, and incentives provided by agricultural and food processing ministries.

8. Sustainable Practices:
Adopt sustainable agricultural practices to ensure long-term viability.
Promote organic farming and eco-friendly processing methods.
9. Financial Planning:
Develop a robust financial plan to manage costs, revenues, and investments.
Explore various funding options such as venture capital, grants, and loans, including government schemes like Mudra loans.

Conclusion
Milletnomics represents a sustainable, resilient, and profitable agricultural ecosystem. By focusing on innovation, technology, strong supply chains, and effective marketing, millet startups can thrive and contribute to the larger goals of food security, environmental sustainability, and rural development. By working in clusters and ensuring uniform pricing, the millet community can achieve greater control over market dynamics and secure better returns for all stakeholders.
With supportive government policies and a growing consumer base, the future of millets looks promising.
IS360 Can be Reached at
Sharing is caring!

