
Ensuring Fair Prices for Millet Farmers through Digitized Agri-Practices
Millet, an ancient grain making a strong comeback, faces a significant challenge: despite rising retail prices, millet farmers often struggle to receive fair compensation for their hard work. This disparity between what farmers earn and what consumers pay threatens the sustainability of millet farming, particularly in regions where it’s a key staple. In this blog, we explore how digitized agricultural practices can help bridge this gap, increase farm yields, and ensure that farmers receive a fair share of the profits. We also discuss how AA Millet Foods and Enterprises Pvt Ltd is leading this transformation through their Quality Maturity Model (QMM) initiative, developed under the 5th Cohort of the Indian Institute of Millet Research (IIMR).
The Price Disparity Problem
Millet farmers often find themselves at the mercy of middlemen, who purchase their produce at low prices only to sell it at a much higher rate in retail markets. This price disparity leaves farmers with meager earnings, discouraging them from continuing to cultivate millet and posing a threat to the broader adoption of this nutritious grain.
The Role of Digitized Agri-Practices
Digitized agricultural practices offer a promising solution to this problem by empowering farmers and improving their market access. Here’s how:
1. Transparent Market Access:
Digitized platforms can connect farmers directly with buyers, eliminating the need for intermediaries. By using mobile apps or online marketplaces, farmers can list their produce and negotiate prices directly, ensuring they receive a fair price.

2. Real-Time Market Information:
Access to real-time data on market prices, demand, and supply helps farmers make informed decisions about when and where to sell their produce. This transparency reduces the chances of exploitation and helps farmers secure better prices.
3. Blockchain for Traceability:
Blockchain technology can be used to track millet from the farm to the consumer. This traceability ensures that the quality is maintained and that consumers can pay a premium for fairly traded millet. Blockchain records verify the authenticity and quality of the produce, which can command higher prices for farmers.
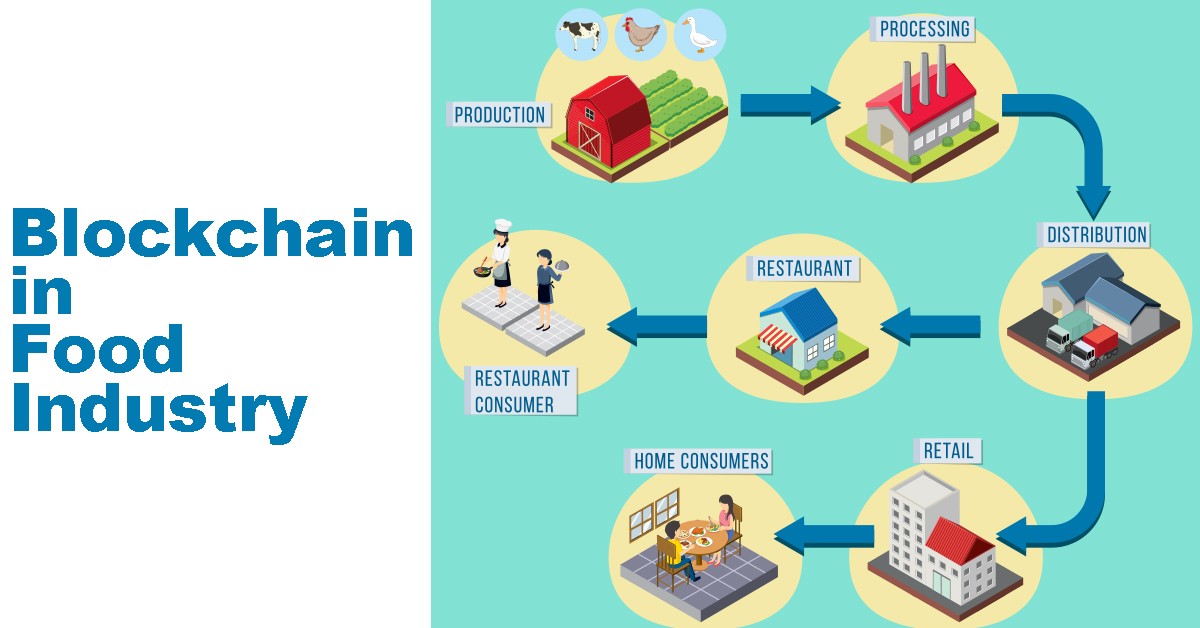
Image credits: Linkedin/BIS Research
4. Precision Farming for Yield Improvement:
Digitized tools like drones, satellite imaging, and IoT sensors monitor soil health, weather, and crop growth in real-time. This data enables precision farming, optimizing inputs like water and fertilizers to increase yields. Higher productivity leads to better market prices and profitability for farmers.
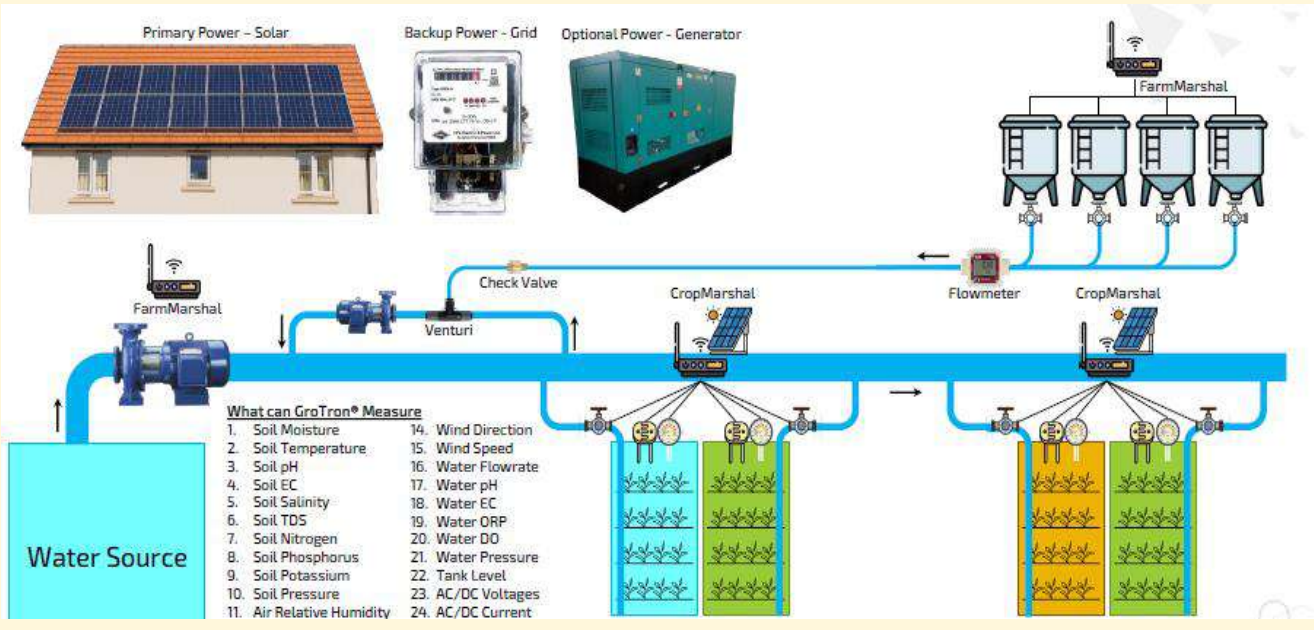
5. Supply Chain Efficiency:
Digitization streamlines the supply chain by reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring that more millet reaches the market in good condition. Efficient logistics and inventory management through digital platforms reduce wastage and improve returns for farmers.
The QMM Initiative: A Game Changer for Millet Farmers
AA Millet Foods and Enterprises Pvt Ltd has taken a pioneering step to address these challenges through their Quality Maturity Model (QMM), developed under the 5th Cohort of the Indian Institute of Millet Research (IIMR). This model introduces a digitized framework that ensures traceability, transparency, and quality throughout the millet value chain.
1. Certified Quality Assurance:
QMM ensures that every batch of millet is traced and certified for quality. Farmers who participate in this program can benefit from higher prices for their quality-assured produce, as consumers are willing to pay more for verified products.

2. 5G Enabled 3D Walkthrough:
As part of the QMM initiative, AA Millet Foods is launching a 5G-enabled 3D Walkthrough of their marketplace. This immersive experience allows consumers and buyers to virtually explore the origin and journey of the millet they purchase, building trust and justifying premium pricing for transparently sourced products.
3. Direct Farmer-Buyer Linkage:
The QMM framework also includes direct linkage between farmers and retailers, cutting out middlemen and ensuring that farmers receive a fair price for their produce. This direct connection is facilitated through digital platforms that enable seamless transactions and communication.

4. Scalable Deployment by IIMR:
Given the success of the QMM initiative, IIMR could consider deploying this model across other regions to support millet farmers nationwide. By scaling up the QMM framework, IIMR can ensure that more farmers benefit from digitized practices, increasing yields and securing fair prices.
A Sustainable Future for Millet Farming
Ensuring that millet farmers receive fair compensation is essential for the sustainability of this vital crop. Digitized agricultural practices, as demonstrated by the QMM initiative from AA Millet Foods, offer a clear path to bridging the gap between farm gate prices and retail prices. With the support and deployment by institutions like IIMR, these practices can be scaled up to benefit more farmers, ensuring that millet continues to be a viable and profitable crop for generations to come.
As consumers, we can support these initiatives by choosing products that guarantee fair trade and by advocating for more transparent and equitable supply chains. Together, we can build a sustainable millet value chain that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment alike.
IS360 Can be Reached at
Sharing is caring!

